Sphenopalatine Ganglion Nerve Block Studies & Resources
Recently the Tx360 has been the center of pilot studies to evaluate the effectiveness of its method to administer a nerve block of the sphenopalatine ganglion nerve (SPG). The study below is of the Tx360 device and technology.
The study concludes that the relief experienced by patients from the techniques used by the MiRx Protocol significantly reduces migraine and head pain.
Tx360TM a Minimally-Invasive Technique for Sphenopalatine Ganglion Nerve Block in the treatment of head and face pain: a case series.
Kenneth D. Candido, MD; N. Nick Knezevic, MD, PhD.; Ruben I. Sauer, Lalida Chupatanakul, MD.
Department of Anesthesiology, Advocate Illinois Masonic Medical Center, University of Illinois, Chicago, IL.
Abstract
The Sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) is located on the posterior aspect of the middle nasal turbinate and has been implicated as a strategic target in the treatment of various head and face pain conditions.
The purpose of this pilot study was to evaluate the effect of the novel, revised method for SPG nerve block with the use of the Tx360.
We are presenting three patients with various head and face pain conditions (post-herpetic neuralgia, chronic migraine, and trigeminal neuralgia). The average baseline NRS pain score was 7. All patients reported significant pain relief within the first 15 minutes post-treatment with an average NRS score of 2. High degree of pain relief was sustained throughout the 28 day follow-up period for 2 of the 3 study participants.
Introduction/Methods
- The literature is rich with different examples of SPG interventions for painful face and head conditions.
- These interventions range from significantly invasive to non-invasive and from cumbersome, technical, and expensive to fast, simple and inexpensive.
- Regardless of the approach, the intent of the SPG intervention is to block or modulate its function thereby eliminating head pain.
- This effect can either be temporary of permanent depending on the technique.
- The transnasal approach is the simplest safest, and least expensive of the SPG interventions. With this technique, a topical anesthetic blocking agent can be delivered to the area of mucosa associated with the SPG.
- The Tx360 overcomes inaccuracy and patient discomfort associated with the long-standing cotton-tip application of transnasal technique.
- In addition, it can be used with deviated septum patients unlike its predecessor.
- After IRB approval three subjects were included, and followed for 28 days with NRS pain score, patient's global impression of change (PGIC) and Modified Brief Pain Inventory Short form )MBPI-sf), satisfaction and use of pain medications.
Results
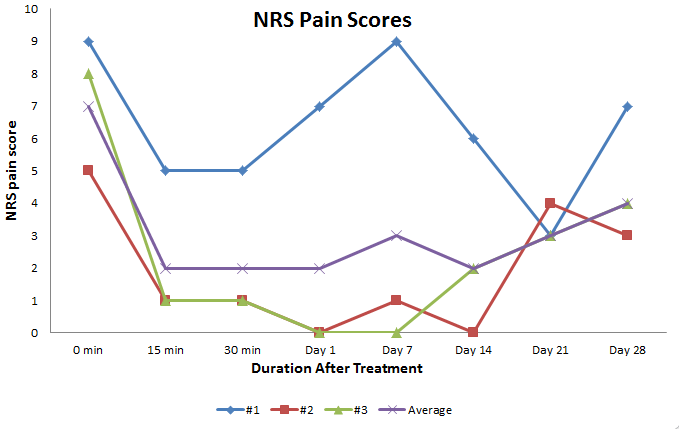
Paitent #1 (Blue)
- A 15-year-old female with two year history of bilateral supraorbital headaches due to postherpetic neuralgia, and post-decompression of Arnold Chiari malformation.
- Pharmacotherapy was attempted for 12 months with no improvements in her symptoms.
- Initial pain level prior to treatment was 9/10
- Result was a drop to 5/10 in 15 minutes sustained for nearly 20 minutes. Repeated treatments made more significant pain relief at day 14 the experience was 3/10 on the NRS.
Patient #2 (Red)
- 18 year-old female with refractory migraines secondary to a fall in 2010. The patient fell on her left head/neck/shoulder area. 10 days later, she started experiencing migraines with the most intense pain being on the left infraorbital region and right supraorbital region.
- Infraorbital and supraorbital nerve blocks were administered. Pharmacotherapy offered marginal temporary pain relief down to a level of 5/10 on the NRS pain scale. The patient had significant improvement during the first two weeks after SPG block.
- After the treatment the pain dropped to 1/10 (NRS) and sustained at or below a 1 for 14 days.
Patient #3 (Green)
- 43-year-old woman presented with daily, paroxysmal, sharp, shooting pain and numbness in her left cheek for the past 18 months.
- A dental consult resulted in a tooth extraction and root canal which did not provide pain relief. Subsequently, the patient was diagnosed with trigeminal neuralgia. Pre-procedure pain level was 8/10 (NRS).
- After the treatment with the Tx360 and sphenopalatine nerve block the pain dropped to 1/10 in 15 minutes, and sustained at or below a 1 for nearly 7 days.
Conclusions
- SPGB with Tx360TM provides rapid clinically significant pain relief with minimal complications at a very low cost.
- As the maximal levels of pain relief were observed to diminish a couple of weeks post-treatment, the efficacy of serial interventions should be investigated.
- Additional studies are needed to assess the efficacy of this technique across the entire spectrum of head and face pain conditions.
- The ease of the Tx360TM should allow for broad potential use beyond the pain specialist, even in the busiest primary care and ER departments.
References
- PiagkuM, et al. The Pterygopalatine Ganglion and its Role in Various Pain Syndromes: From Anatomy to Clinical Practice. Pain Pract. 2011;29:1-4
- Yarnitsky D, et al. 2003 Wolff Award: Possible parasympathetic contributions to peripheral and central sensitization during migraine. Headache 2003;43: 704-14
- Maizels M, et al. Intranasal lidocane for migrane: A randomized trial and open-label follow-up. Headache 1999;39: 543-51
Additional SPG Nerve Block Resources:
1.) Rapid and sustained relief of migraine attacks with intranasal lidocaine: preliminary findings.
Headache. 1995 Feb;35(2):79-82. Kudrow L, Kudrow DB, Sandweiss JH.
California Medical Clinic for Headache, Encino 91436, USA.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7737865
2.) Intranasal Lidocaine for Treatment of MigraineA Randomized, Double-blind, Controlled Trial
Morris Maizels, MD; Barbara Scott; Wendy Cohen, MD; Wansu Chen, MS
JAMA. 1996;276(4):319-321. doi:10.1001/jama.1996.03540040063034.
http://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=405844
3.) Sphenopalatine ganglion block: a safe and easy method for the management of orofacial pain.
Peterson JN, Schames J, Schames M, King E.
Source: Headache and Pain Center, Hollywood Community Hospital, Los Angeles, CA 90028, USA.
Cranio. 1995 Jul;13(3):177-81.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8949858
4.) Over 3 Million Look to Hospitals for Headache Relief, Particularly for Migraines
AHRQ News and Numbers, May 4, 2011
http://www.ahrq.gov/news/newsroom/news-and-numbers/050411.html
5.) A new interest in an old remedy for headache and backache for our obstetric patients: a sphenopalatine ganglion block
S. Cohen, S. Trnovski, Y. Zada Article first published online: 26 JUL 2007
DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2001.2094-34.x
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-2044.2001.2094-34.x/full
6.) Intranasal lidocaine 8% spray for second-division trigeminal neuralgia
A. Kanai*, A. Suzuki, M. Kobayashi and S. Hoka
- Author Affiliations - Department of Anesthesiology, Kitasato University School of Medicine1-15-1. Kitasato, Sagamihara 228-8555, Japan



